로컬,개발,운영 yml를 하나로 통합 및 yml 호출하여 사용하는 방법에 관해서
server:
port: 8098
file:
watch:
path: C:\\test_config기존에는 yml 파일들을 local, dev, prod로 분리하였다.
설정 정보들이 많은 경우는 헷갈리기 때문에 따로 분리를 해두지만,
설정 정보가 극히 적은 경우 하나의 yml 관리하는것이 편한경우도 있다.
본 글은 하나의 yml에서 분리하여 사용하는 방법을 소개한다.
다중 프로파일 YAML 문서에 따르면 한 곳에서 spring.profiles 옵션을 통해서 분리하여 운영이 가능하다.
Spring Boot 2.4 이전 버전에서 properties 파일로 Spring Boot 설정을 할 때는 프로파일 별로 properties 파일을 따로 만들어야 했으나, Spring Boot 2.4버전부터는 위와 같이 하나의 파일에 여러 프로파일을 설정하고 #---를 사용하여 각 프로파일을 구분할 수 있게 되었다.
yml에서는 ---로 구분할 수 있다.
server:
port: 8080
---
spring:
profiles: local
server:
port: 8097
file:
watch:
path: C:\\test_config
---
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 8096
file:
watch:
path: C:\\test_config
---
spring:
profiles: prod
server:
port: 8095
file:
watch:
path: C:\\test_configactive한 yml이 명시적으로 선언되지 않은 경우 서버는 디폴트로 8080 포트로 실행이 된다.
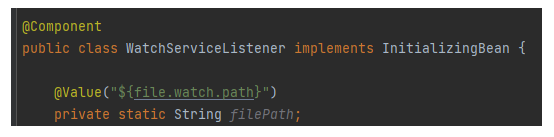
외부 프로퍼티 호출시 @Value("${...}") 의 사용은 별로일수도..
@Value 어노테이션은 대게 SPEL과 같이 사용한다. 그러나 단점이 있다. yml의 사용해야할 프로퍼티의 값이 없는 경우NPE를 발생시킨다,
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 8096
file:
watch:
path:
로그만 봤을때 해당 클래스의 어딘가 NPE가 터졌다 라고 유추 해 볼수 있지만 한눈에 들어오지는 않는다.
나는 필수 설정 정보 값을 기입 하지 않는 다면 꼭! 기입을 해라! 라고 간단 명시적으로 exception에서 알려주고 싶다.
@Valid 를 통해서 프로퍼티도 검증해주자.
의존성 추가
dependencies {
annotationProcessor "org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-configuration-processor"
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-validation:3.1.2'
}application.yml
file:
watch:
path: C:\\test_configWatchProperties.class
@Getter
@Setter
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="file")
@Validated
@Configuration
public class WatchProperties {
private String path;
private Watch watch;
@Getter
@Setter
public static class Watch{
@Valid
@NotNull(message = "널이면 안돼요")
@NotBlank(message = "빈칸이면 안돼요")
private String path;
}
}클라이언트 코드
@Autowired
private WatchProperties watchProperties;
public void test(){
...
watchProperties.getWatch().getPath()
...
}
프로퍼티의 이름, 해당 라인, 이유 까지 정말 친절하게 알려준다.
다만 @Setter 를 사용하기 때문에 불변성이 깨지는 꺼림직한점이 남아있긴하다. 만약 이 방법을 사용한다면 해당 클래스는 절대로 set을 사용하지 않기로 약속을 하자..
setter를 지워볼까??
@ConstructorBinding 어노테이션을 이용함으로써 불필요한 setter를 사용하지 않게 되면서 불변성을 유지할 수 있게 된다.
WatchProperties 클래스는 Spring Bean 으로 만들어주지 않기 때문에 @Configuration 사용하여 빈으로 등록해주자.
PropertiesConfiguration.class
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = {WatchProperties.class})
public class PropertiesConfiguration {
}WatchProperties.class
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@ConstructorBinding
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="file")
@Validated
public class WatchProperties {
private final Watch watch;
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public static final class Watch{
@Valid
@NotNull(message = "널이면 안되요")
@NotBlank(message = "빈칸이면 안되요")
private final String path;
}
}단점은 WatchProperties.class을 스프링 빈으로 등록시키기 위해서 매핑 클래스를 만들어주어야 한다(PropertiesConfiguration.class)
공식문서
Note: To use constructor binding the class must be enabled using @EnableConfigurationProperties or configuration property scanning. Constructor binding cannot be used with beans that are created by the regular Spring mechanisms (e.g. @Component beans, beans created via @Bean methods or beans loaded using @Import).상황에 맞게 골라서 적용하자.
추신
springboot 3.0 부터 @ConstructorBinding 을 사용을 못한다고 한다

참고자료
https://www.latera.kr/reference/java/2019-09-29-spring-boot-config-externalize/
https://tecoble.techcourse.co.kr/post/2020-09-29-spring-properties-binding/
